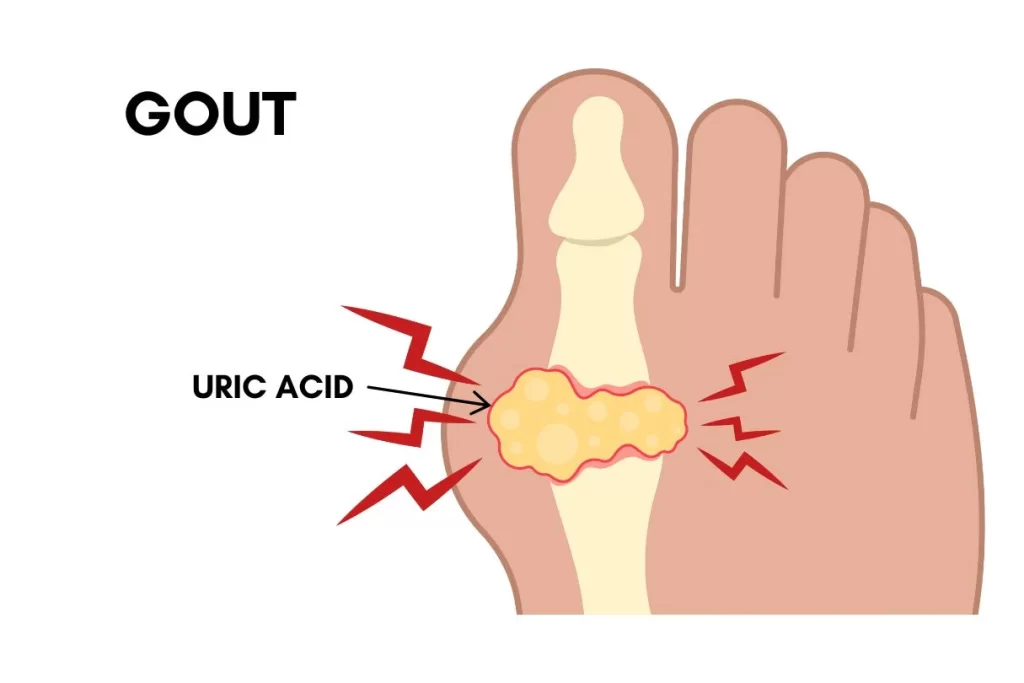
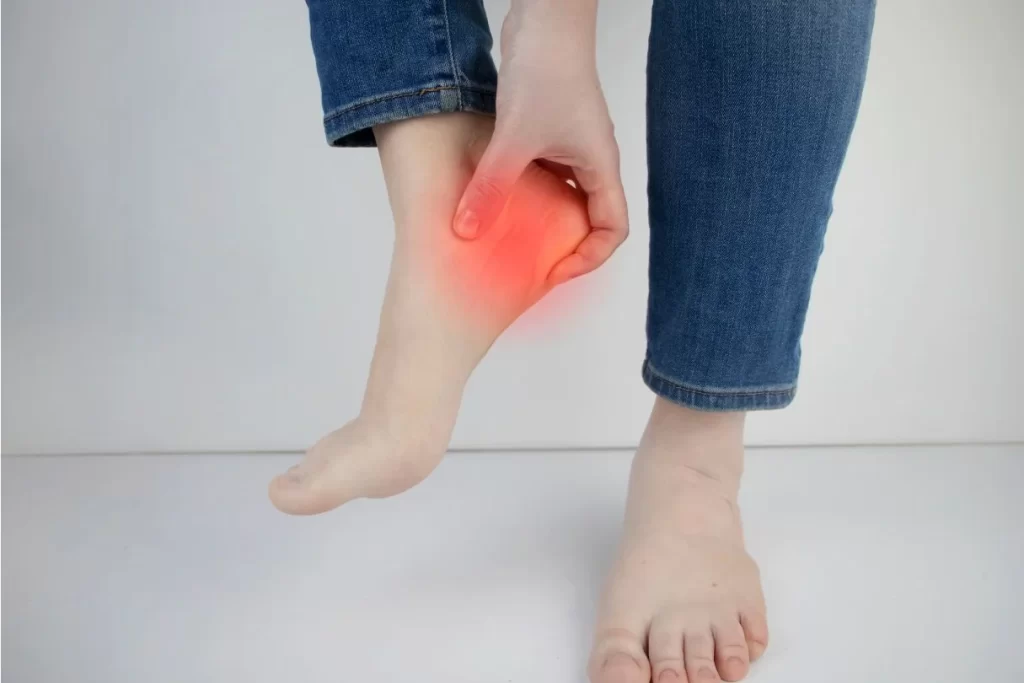
Causes of Gout
Gout is a result of an excess of uric acid in the blood. Normally, uric acid is excreted through urine, but when the body produces too much or fails to eliminate enough, it can crystallise and deposit in the joints. These uric acid crystals trigger your body to attack its joints, causing pain and inflammation.
The causes of increased uric acid levels include:
- Diet: High intake of purine-rich foods like red meat, shellfish, and alcohol can elevate uric acid levels.
- Genetics: Some individuals inherit a predisposition to developing gout due to genetics.
- Dehydration: Not drinking enough water can make it harder for the body to flush out excess uric acid.
- Kidney Dysfunction: Impaired kidney function can reduce the body’s ability to eliminate uric acid.
- Obesity: Being overweight increases the risk of having high uric acid levels in the body
Need Help? See Our Podiatrist Today
Signs and Symptoms of Gout
The signs and symptoms of gout usually appear suddenly and can be severe. Common symptoms include:
- Intense Joint Pain: The pain often begins suddenly, especially at night, and typically affects the big toe but can involve other joints in the lower limbs, such as the ankles and knees.
- Swelling and Redness: The affected joint may become swollen, red, and hot to the touch.
- Tenderness: Even the lightest touch can cause intense pain in the affected joint.
- Burning Sensation: At times the pain can be so severe that it feels like your toe or foot is on fire.
- Stiffness: As the inflammation worsens, the affected joint’s range of motion becomes restricted.
Risk Factors for Gout
-
There are several factors that can increase your risk of developing gout, particularly in the lower limbs:
- Diet: A diet high in purines, found in foods such as organs, seafood, and alcohol, especially beer, can increase the risk.
- Obesity: Excess weight lead to higher uric acid levels in the body, increasing the likelihood of gout.
- Age and Gender: Men are more likely to develop gout, particularly in middle age between 30 and 60. Women are at increased risk after menopause.
- Medical Conditions: High blood pressure, diabetes, kidney disease, and heart disease can contribute to higher uric acid levels.
- Medications: Certain diuretics and aspirin can also cause higher uric acid levels in the body.
Gouty Arthritis
Gouty arthritis is a form of infammatory joint disease that occurs when uric acid crystals accumulate in the joints. It leads to joint inflammation and pain. It most commonly affects the lower limbs, with the big toe being the most frequently impacted joint. Over time, recurrent gout attacks can lead to joint damage and a condition known as chronic gouty arthritis, where the joints may become permanently damaged.
A person with chronic gouty arthritis will have restrictions in the range of motion of the affected joint. The restriction will impact the person’s mobility and gait functions. As a result, it can lead to secondary musculoskeletal problems. For example, restriction in the big toe joint often causes metatarsalgia or plantar plate injury of the second toe joint.
In some cases, gout can also lead to the formation of tophi (uric acid crystal deposits) under the skin, particularly around the joints. This condition is known as tophaceous gout. These lumps can be painful and unsightly. Over-accumulation of these crystals can also cause the tophi to break down and form chronic wounds. Such cases of tophaceous gout will require more invasive treatment to prevent further complications.
Treatment Options for Gout
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Medications like ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce inflammation and pain during a gout attack.
- Colchicine: This medication helps reduce inflammation and can help manage acute gout attacks if treatment is started early.
- Corticosteroids: In cases where oral medications are ineffective, your GP may prescribe corticosteroid injections to control the inflammation.
- Rest and Elevation: Resting and elevating the foot can help reduce swelling and provide relieve.
- Ice Therapy: Applying ice to the affected joint can help alleviate pain and reduce swelling.
Long-Term Management
Long-term management is necessary to prevent future gout attacks and preserve your joint health. It typically includes:
- Uric Acid-Lowering Medications: Drugs such as allopurinol or febuxostat, as prescribed by your GP, help lower uric acid levels and reduce the risk of gout attacks.
- Lifestyle Changes: Staying hydrated, having balanced diet, and weight management can help control uric acid levels.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular blood tests to monitor uric acid levels are essential to long-term gout management.
Diet Recommendations for Gout
Diet plays a significant role in managing gout. To reduce the risk of flare-ups, we recommend seeing a Dietitian or the following:
- Limit Purine-Rich Foods: Foods such as red meat, organ meats, and certain seafood (e.g., crabs, shrimps) should be limited.
- Avoid Alcohol: Alcohol, particularly beer, can increase uric acid levels and raises risk of triggering gout attacks.
- Drink Plenty of Water: Staying hydrated helps the kidneys excrete uric acid more efficiently.
- Increase Low-Purine Foods: Foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products are beneficial for individuals with gout
When to See a Podiatrist?
It is important to consult a podiatrist if you are experiencing gout symptoms, particularly in the lower limbs. A podiatrist can:
- Assess whether your symptoms are resulting from gout or another condition.
- Provide guidance on managing gout attacks and referral for medications.
- Recommend lifestyle changes to prevent future flare-ups.
- Offer a customised management plan, including foot orthotics or footwear recommendations to relieve pressure on the affected joints.
If you are experiencing recurrent gout attacks or persistent pain in your lower limbs, it is time to seek help. At Straits Podiatry, we strive to help you manage gout and maintain optimal foot and joint health.
Conclusion
Gout is a painful inflammatory joint condition that typically affects the ankle and foot, especially the big toe joint. Therefore, you should start taking early measures to prevent long-term complications.
At Straits Podiatry, our experienced podiatrists are here to provide personalised care for gout and help you maintain a healthy, active lifestyle. We also work closely with specialists to help manage your uric acid levels. If you’re experiencing gout symptoms, schedule an appointment with us today.
Share this with someone you know
Search
You May Also Like
Do You Have A Question? Ask Us...
Search
Do You Have A Question? Ask Us...
You May Also like
Categories
Categories
- Ankle (4)
- Diabetic Foot (7)
- Feet (5)
- Knee (5)
- Paediatric Lower (5)
- Soft Tissue (3)
- Uncategorized (60)