Overview of Flat Feet
Flat feet, or medically termed as pes planus, is a condition where the arches of the feet are lower than normal or completely collapsed. In severe cases, the entire sole of the foot will completely touch the ground. Although many people with flat feet experience no symptoms, others may face significant discomfort and long-term complications. Flat feet with symptoms typically warrant treatment to manage the pain and prevent further complications.
Flat feet occur when the foot arch either does not develop properly or collapses over time. It is a common foot deformity condition seen in Asian countries. Flat feet in children (paediatric pes planus), especially infants and toddlers, can be normal as the arches typically develop during childhood. However, flat feet that persist into adulthood or develop later in life can lead to various foot and lower limb problems, including pain, fatigue, and difficulty walking.
Importance of Foot Arch
The arch of the foot is a key player in foot biomechanics, as it acts as a structural stabiliser when you walk, run, and stand. It also helps distribute your weight across the entire foot like a tripod, and it helps transfer load effectively from the heel to the forefoot. When the arch collapses or fails to hold its shape, the foot functions change, and the gait pattern is affected. As the foot function directly affects the walking pattern, fallen arches can lead to potential problems up the lower limbs, including the feet, ankles, knees, and even the hips or lower back. Therefore, addressing flat feet early is essential to prevent injuries and maintain overall foot health and mobility.
Need Help? See Our Podiatrist Today
Causes of Flat Feet
A person can develop flat feet for various reasons, including:
- Genetics: Some individuals inherit the foot structure from their parents. It’s often congenital, meaning the condition is present from birth.
- Weak or Stretched Tendons: The posterior tibial tendon supports the arch of the foot. If this tendon becomes weak or damaged, it can cause the arch to collapse.
- Injury: Trauma or injury to the foot or ankle, such as Lisfranc fractures or ankle sprains, can weaken the structure of the foot and lead to arch collapse.
- Ageing: As individuals age, the tendons and ligaments in the feet may lose elasticity and weaken, leading to the collapse of the arch.
- Obesity: High body mass places additional load on the feet, which can lead to the flattening of the arch.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can cause ligaments to be loose, contributing to the development of arch collapse, especially in women with a predisposition.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, tarsal coalition, and Charcot’s foot can affect the structure of the foot and contribute to flat feet.
Types of Flat Feet
There are four primary types of flat feet:
- Flexible Flat Feet: This is the most common type, where the arch appears when the person is sitting, but the arch flattens when standing or walking. Flexible flat feet are relatively easier to manage using conservative options.
- Rigid Flat Feet: In this case, the arch is flattened when sitting and standing and does not return to its normal shape. Rigid flat feet typically indicate a more serious underlying problem (e.g. tarsal coalition) and may require more intensive treatment.
- Congenital: While flat feet at birth are normal, certain cases require immediate attention as they may lead to functional issues in infants and toddlers. A rare example is congenital vertical talus, where the talus bone is fixed in an abnormal position, causing a fixed foot deformity.
- Acquired (Adulthood): This is typically a result of weakened ligaments and tendons, resulting in the collapse of the foot arch during adulthood. The most common condition causing this is posterior tibial tendonitis, especially when left untreated.
Signs and Symptoms
While some individuals with flat feet may not experience any symptoms, others may encounter various problems. Common symptoms include:
- Foot Pain: This is the most common complaint, especially in the arch or heel area.
- Swelling: Swelling along the inside of the foot and ankle, particularly after long periods of standing or walking.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired in the legs and feet after physical activity.
- Pain in the Knees, Hips, or Lower Back: Flat feet can cause misalignment in the knees, hips, and lower back, resulting in additional pain.
- Difficulty with Footwear: Finding shoes that fit properly may become a challenge, especially if the foot is wider than usual due to the collapse of the foot arch
Secondary Conditions Associated with Flat Feet
Flat feet can lead to various conditions, especially if you neglect your foot health. While some individuals may only suffer pain later in life, some may develop these conditions as early as in their teens.
Associated conditions, as seen in research, include:
- Posterior tibial tendonitis
- Plantar fasciitis
- Achilles tendonitis
- Sinus Tarsi Syndrome
- Shin Splints
- Peroneal Tendonitis
- Runner’s knee (Patellofemoral pain syndrome)
- Iliotibial Band Syndrome
Treatment Options for Flat Feet in Singapore
Treatment options to manage flat feet typically depend on the severity of the condition and the symptoms. Standard treatment options include:
- Footwear Adjustments: Wearing shoes with good arch support and cushioning can help alleviate discomfort and reduce strain on the feet. Orthotic insoles may also be necessary to provide extra support and correct alignment.
- Physical Therapy: Stretching and strengthening exercises can help improve foot flexibility and strengthen the muscles supporting the arch. Exercises may target the calves, Achilles tendon, and the posterior tibial tendon.
- Orthotics: Custom-made insoles can help realign the foot, support the arch and reduce pain by redistributing pressure across the foot. These devices can be especially helpful for individuals with flat feet caused by weak tendons.
- Pain Relief: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help manage pain and inflammation associated with flat feet. Ice therapy may also help reduce swelling.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the strain on the foot and help manage flat feet symptoms.
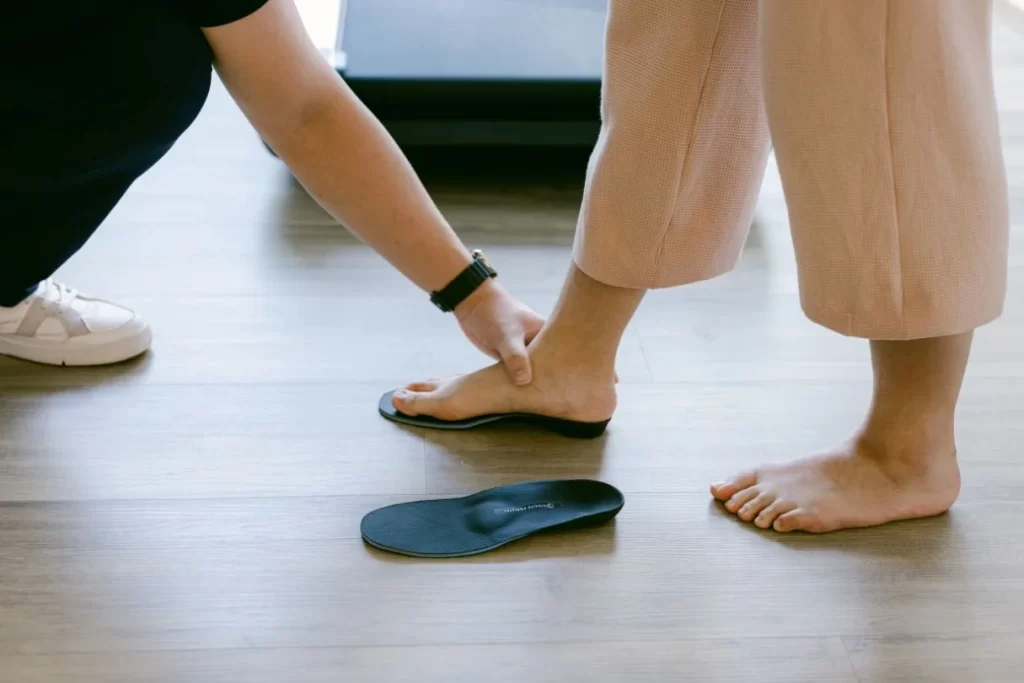

Is Surgery Necessary?
In most cases, surgery is not necessary for treating flat feet. However, surgery may be beneficial if:
- Conservative treatments have not provided sufficient relief.
- There is significant pain, difficulty walking, or decreased quality of life due to flat feet.
- There is significant tendon dysfunction or structural damage that only surgery can correct.
Common surgical procedures include tendon repair, realignment of the bones, or fusion of the joints in extreme cases. Surgery is usually considered a last resort when all other treatments have been exhausted.
When to See a Podiatrist?
If you experience pain, discomfort, or difficulty walking due to flat feet, it’s important to consult a podiatrist for an evaluation. A trained podiatrist will be able to differentiate the type of foot deformity, perform gait assessment, and recommend appropriate flat feet treatment options to help manage your concerns. You should see a podiatrist if:
- You experience persistent foot pain or swelling.
- You have difficulty finding comfortable shoes or wearing shoes.
- Your symptoms interfere with your daily activities or quality of life.
- You notice pain in other parts of the body, such as your knees, hips, or lower back.
Conclusion
Flat feet or pes planus can cause a range of issues, from mild discomfort to significant pain and functional limitations. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available can help you manage the condition and prevent complications. If you’re experiencing symptoms or struggling with foot pain, don’t hesitate to seek help from a professional. At Straits Podiatry, our team of expert podiatrists is here to provide personalised care and support for all your foot health needs. Contact us today to schedule an appointment and get back on the path to healthy, pain-free feet.
Frequently Asked Questions on flat feet
Can flat feet cause pain in other parts of the body?
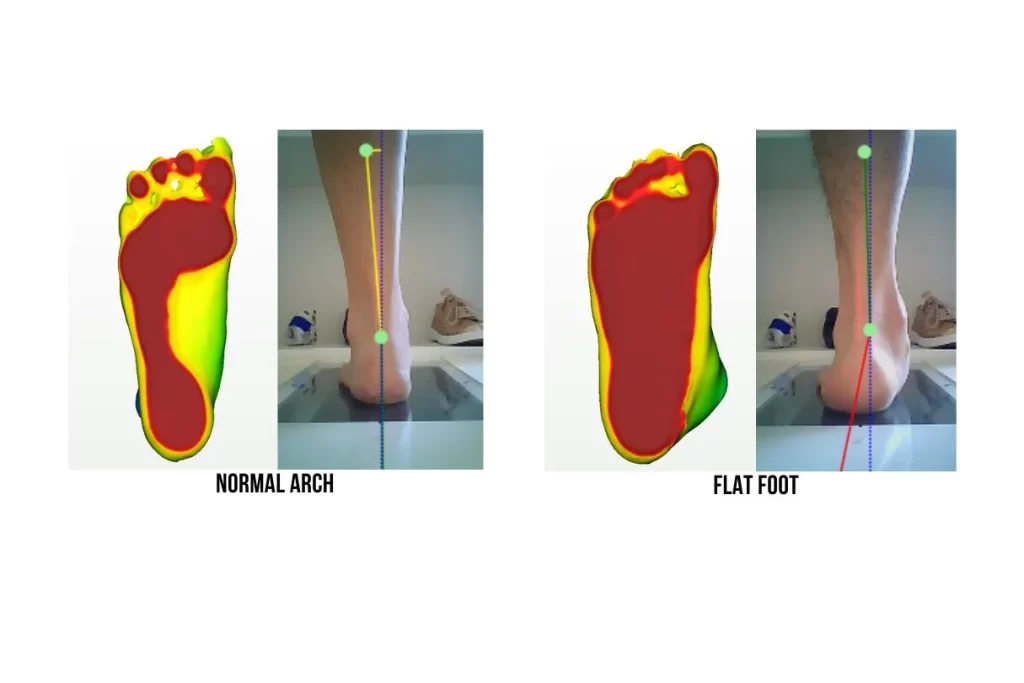
There are a few methods for assessing whether you have a normal foot arch. You can either observe your footprints, check the wear pattern of your shoe, or look from the back of your heels.
1. Check Your Footprints
Footprints are one of the easiest ways to assess your foot arch. A normal footprint would have an obvious concave curvature at the arch. A person with flat feet would not have a concave curvature or may be convex.
2. Check The Wear Pattern of Your Shoe
A person with flat feet will have a medially distorted shoe upper, meaning the arch area bulges outwards. You will also notice that the heel counter starts to slant inwards. Excessive wear of the inner side of the sole is also a key sign.
3. Look From The Back of Your Heels
The ideal foot posture is to have a vertical heel position. A person with flat feet typically has an inward slanting heel position (forming a triangle), whereas high arch feet may have an outward slanting heel position (inverted triangle).
Can Flat Feet be Corrected Permanently?
There are methods to correct flat feet permanently, the majority through surgical options. However, there are paediatric cases where the foot structure improves with the use of supramalleolar orthoses. Generally, conservative methods will no longer work once you reach adolescence or adulth
Can flat feet develop later in life?
Yes, flat feet can develop later in life due to factors such as ageing, injury, or certain medical conditions. It’s important to address symptoms early and seek professional evaluation to prevent further issues.





