Overview
Foot pain is a common ailment that affects millions of people worldwide, with a prevalence rate of up to 36%1. From a dull ache that comes and goes to sharp pain that makes walking difficult, the experience can vary from person to person. In a city like Singapore, where people are often on the move for work, school, or daily errands, even minor foot issues can start to interfere with daily life. That’s why it’s important to recognise foot pain symptoms early, understand the underlying cause, and seek timely care from a podiatrist.
What Is Foot Pain?
Foot pain is a broad term that describes discomfort or pain in one or more areas of the foot. This can include the toes, arches, heels, and soles. This pain can present in various forms, such as sharp or stabbing sensations, dull aches, throbbing, tingling, numbness, or burning. Foot pain can affect individuals of all ages and backgrounds, and its impact on daily life can also vary widely.
Need Help? See Our Podiatrist Today
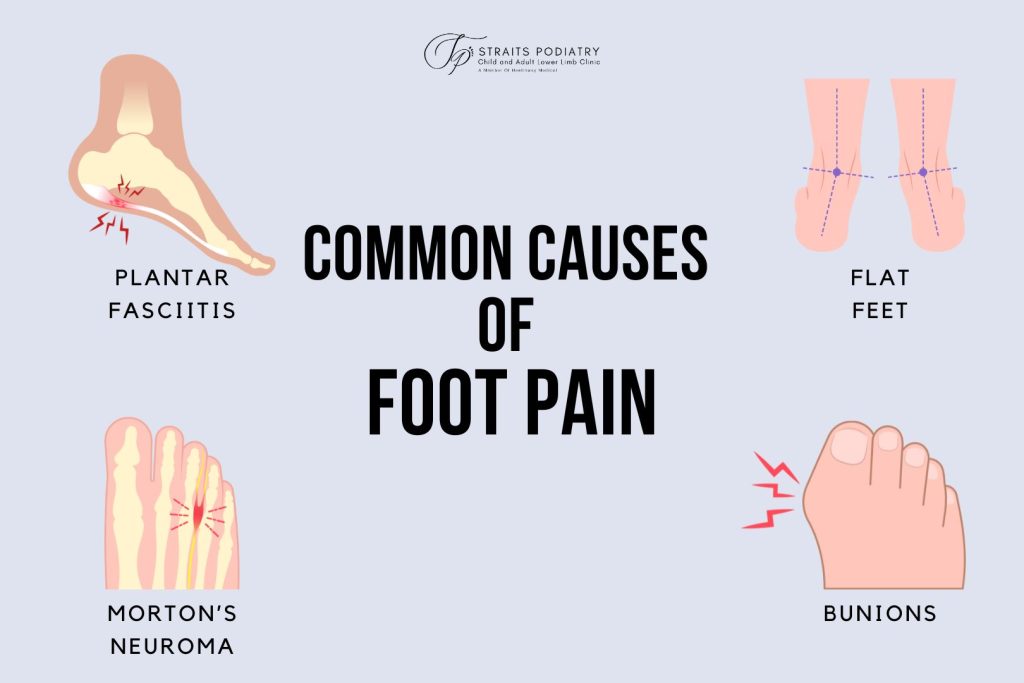
Common Causes of Foot Pain
Pain at the ball of the foot:
- Metatarsalgia: Refers to pain in the ball of the foot, often caused by repetitive stress. It tends to flare up during activities like hiking, running, or prolonged standing.
- Morton’s Neuroma: An inflammation of a nerve that causes pain and numbness shooting to the toes.
- Plantar Plate Injury: A toe joint injury that causes pain and retraction of the toe, commonly seen in middle-aged females.
- Stress Fracture: A hairline crack on the metatarsal bones, usually seen in athletes or long-distance runners.
Pain at the arch of the foot:
- Posterior Tibial Tendonitis: An inflammation of the posterior tibial tendon that causes pain, swelling, and redness at the arch or the ankle. It is a condition that can result in flat foot deformity if it is not treated early.
- Tibialis Anterior Tendonitis: An inflammation of the tibialis anterior tendon that usually causes pain when pointing the foot up.
- Midfoot Arthritis: Inflammation and degeneration of the joints in the midfoot, resulting in pain, stiffness, and swelling.
- Plantar Fascia Strain: An overuse injury of the plantar fascia that causes splitting pain in the arch, typically worse on the first step after rest.
Heel Pain:
- Plantar Fasciitis: an inflammation of the plantar fascia, causing the heel to hurt, especially during the first steps in the morning after waking up.
- Insertional Achilles Tendonitis: An inflammation at the junction between the Achilles Tendon and the heel bone.
- Heel Spur: Bony spurs growing on the heel bone as a result of calcium deposits
- Fat Pad Syndrome: A contusion of the heel fat pad, causing aches or bruised sensation at the heel
- Baxter’s Nerve Entrapment: A nerve compression affecting the heel that causes pain, burning and numbness of the heel.
Pain at the toes:
- Bunions: Abnormal bony growths at the big toe joint that can cause pain and discomfort, especially when wearing tight-fitting shoes.
- Sesamoiditis: Inflammation of the sesamoid bones under the big toe joint, usually as a result of overuse and commonly seen in ballet dancers or sprinters.
- Turf Toe: An injury when the toe is forcefully bent too far, resulting in bruises and pain.
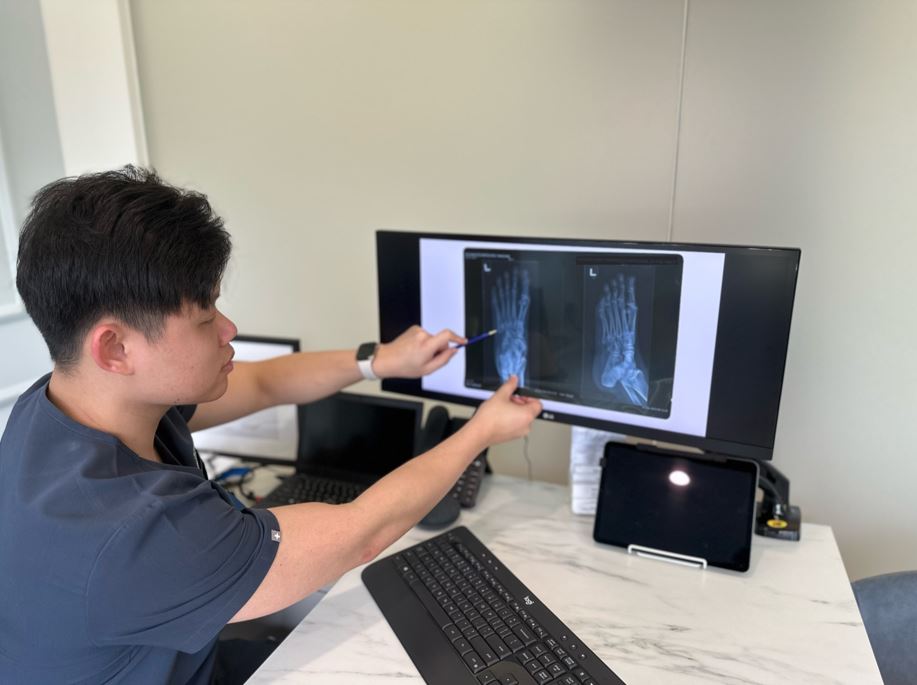
Diagnosis
- Patient Interview: Listening and understanding your problem and symptoms is crucial in determining possible diagnoses.
- Physical Examination: To identify tender areas and check the foot’s appearance for possible underlying causes.
- Imaging: Diagnostic ultrasound, X-rays, or MRI may be necessary to visualize bones and soft tissues, aiding in diagnosing your condition.
- Blood Tests: You may be referred for these tests to help identify underlying systemic conditions such as gout or rheumatoid arthritis.
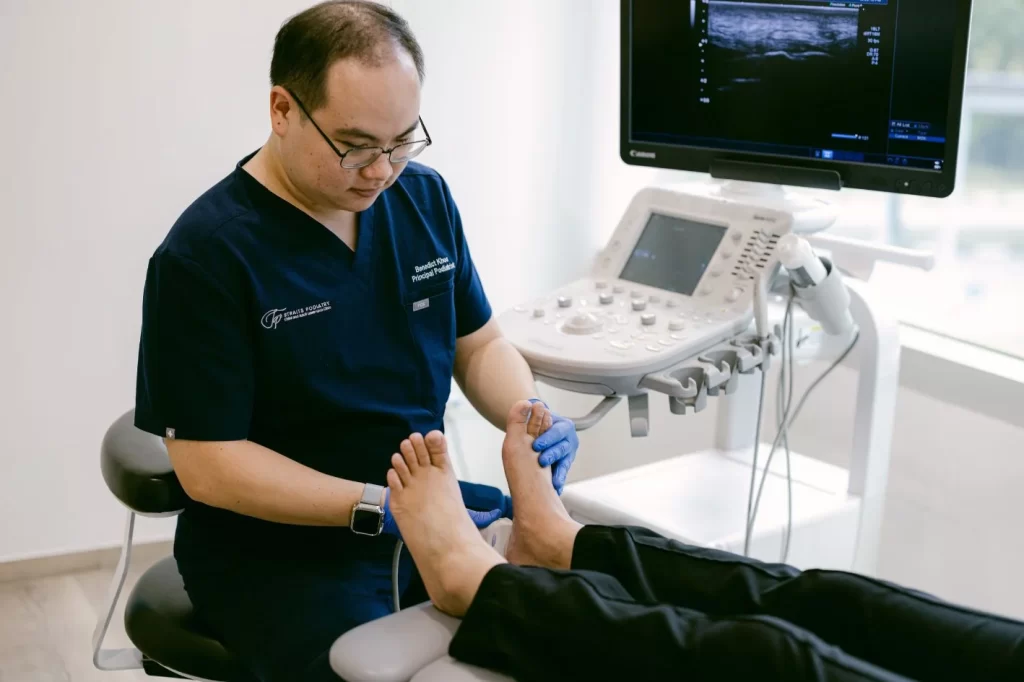
Treatment Options for Foot Pain in Singapore
This is dependent on its cause and severity. Generally, the standard treatment options include:
Conservative Management:
- Lifestyle changes: Reduce activity, switch to lower-impact sports, and wear supportive footwear.
- Rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE): This helps with swelling reduction, especially after an acute injury.
- Over-the-counter Medications: Non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs or topical creams may help to reduce pain and inflammation. Still, it is recommended to speak to your doctor before taking them.
- Stretching and strengthening exercises: Improves flexibility and strength of the muscles to reduce stress on tendons and joints.
- Orthotic devices: Customised foot orthoses or ankle-foot orthoses may be necessary to offload injured tendons or joints and improve pain and functions.
- Shockwave therapy: A conservative therapy that stimulates the body’s natural healing process.
- Electromagnetic therapy: Reduces pain and inflammation and increases cell metabolism.
Surgery is typically only necessary when conservative management does not show any improvement. The common surgical procedures are tendon repair or release, foot deformity correction, or bunionectomy.
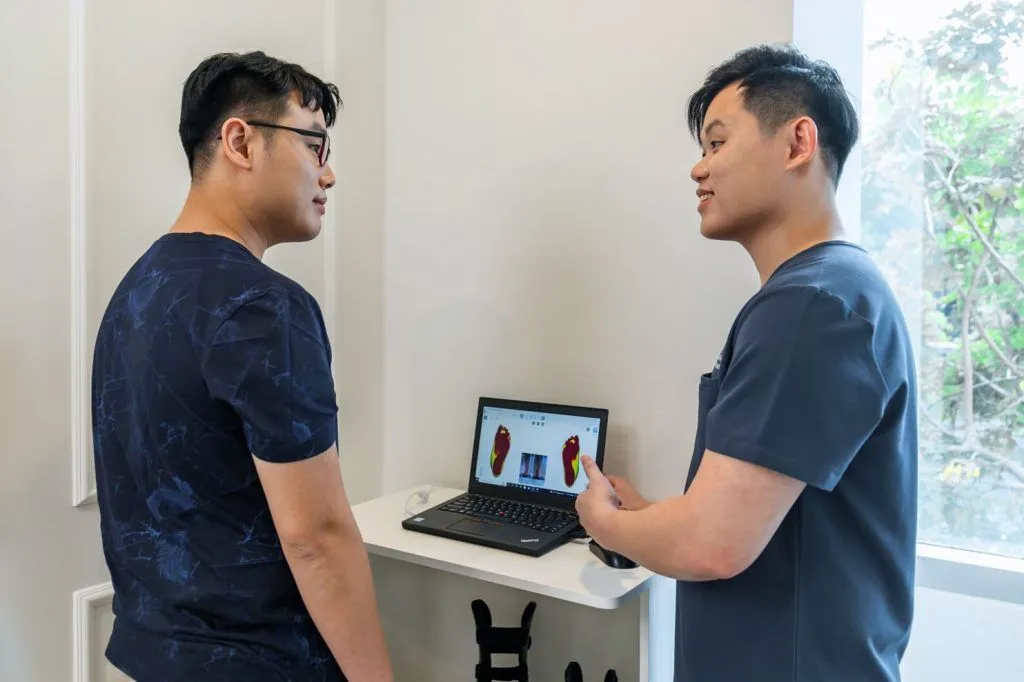

How Can Podiatry Help with Foot Pain?
Don’t let foot pain hamper you from enjoying your daily activities any longer. Book an appointment with us today.
Share this with someone you know
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Acute or Chronic Foot Pain?
Acute foot pain occurs suddenly and is often due to a specific incident or injury. It can result from activities like sports, accidents, or falls.
How Do I Know if My Foot Pain is Serious?
You should seek help as soon as possible if you have:
- Significant swelling and bruising of the foot
- Pain that is unbearable to stand or walk
- Lost the ability to control and movement of your foot
- Pain that has persisted over a week without any signs of improvement
- Pus discharging from a wound with surrounding redness and swelling
Who Should I See if I Have Pain in My Foot?
You should consult a podiatrist or a foot and ankle specialist if you are experiencing any discomfort with your feet. Seeking help early will not only give you a higher chance of quick recovery but also help prevent pain from turning chronic.
How Can I Prevent Foot Injury?
Preventing foot pain requires discipline and a proactive approach to making lifestyle changes, such as:
- Wear the right shoe: Choosing comfortable, supportive shoes (e.g. sports shoes) that fit well is crucial.
- Maintain good foot hygiene: Keeping feet clean and changing socks daily can help prevent painful infections.
- Exercise regularly: Going for long walks or runs can help improve overall health. Performing regular stretching and strengthening exercises can also prevent injuries.
- Managing underlying conditions: Controlling systemic conditions through prescribed medications is crucial in preventing any painful flare-ups.
- Seek medical attention early: Seeking help at the first signs of foot discomfort or pain.
Can I Continue My Activity if I Have a Minor Foot Injury?
Healer provides expert medical services, including primary care, pediatric care, and telemedicine options.