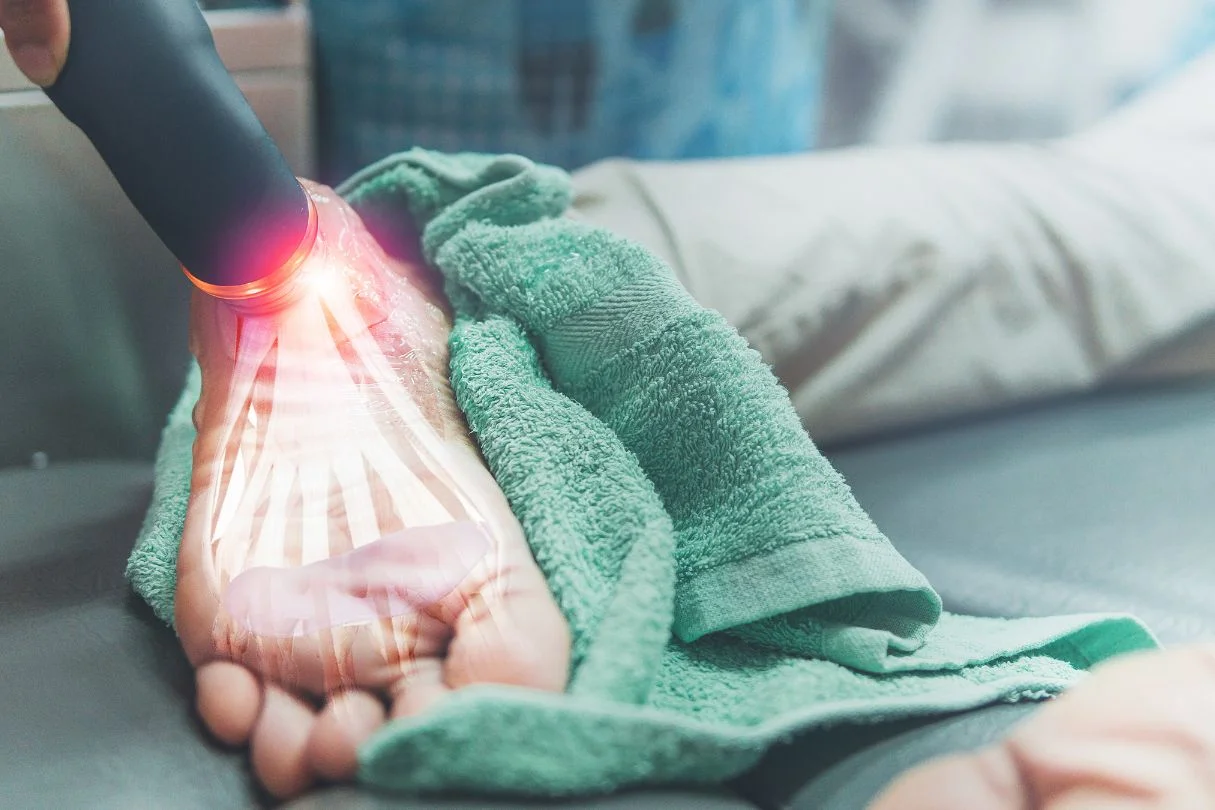
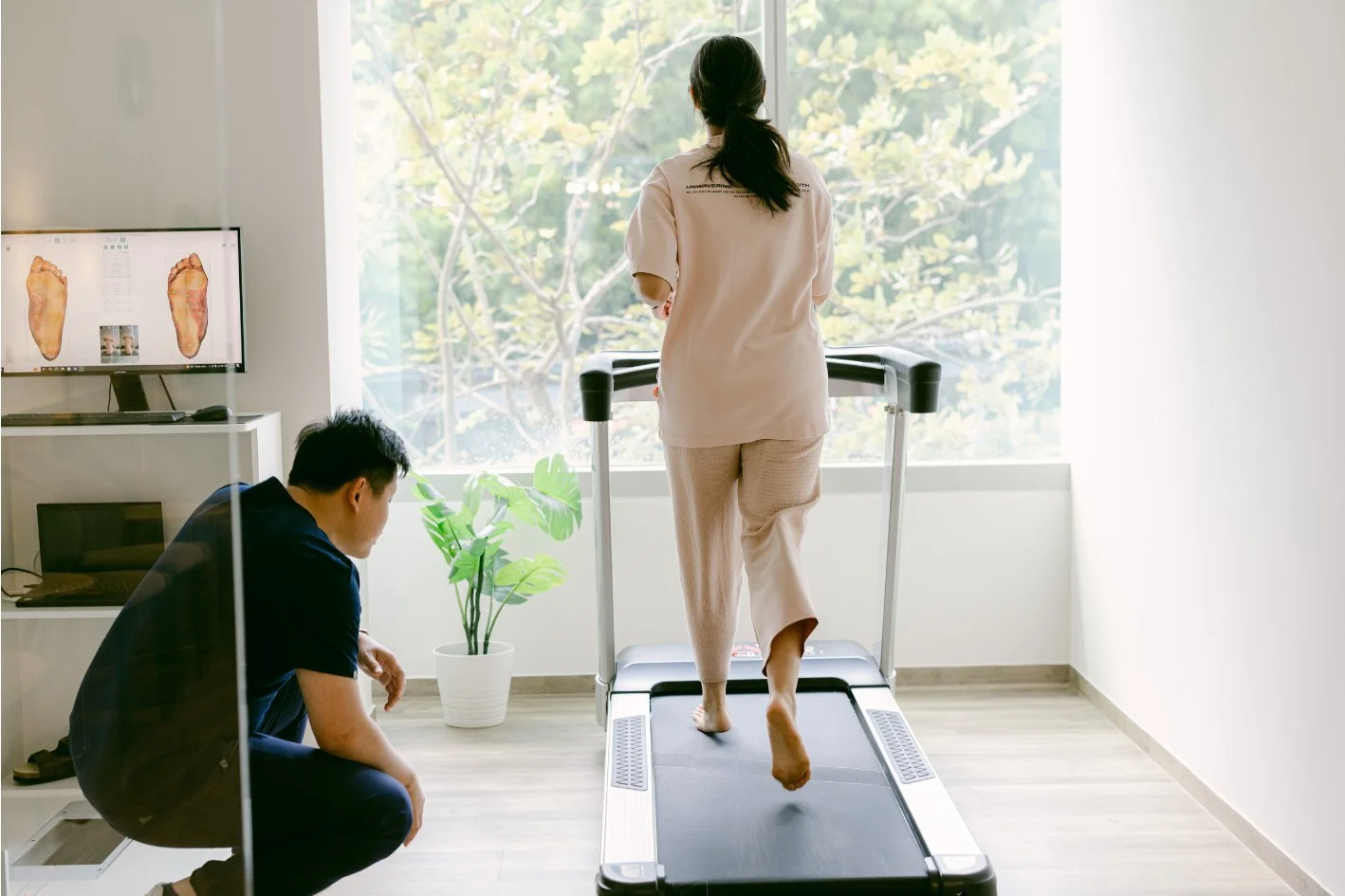
The plantar fascia is a crucial part of the foot structure that plays a significant role in maintaining stability and supporting movement. When the plantar fascia becomes injured or inflamed, it can lead to substantial pain and discomfort, commonly known as plantar fasciitis. Understanding the functions of the plantar fascia, the causes of inflammation, and how to prevent injury can help you better manage this condition and improve foot health.
At Straits Podiatry, we are dedicated to helping patients with plantar fascia-related issues by offering comprehensive care and treatment options.
What is Plantar Fascia?
The plantar fascia is a thick, fibrous band of tissue that runs along the bottom of your foot, holding your heel bone to the toes together. It acts as a pillar for the foot, cushioning the impact of walking, running, and jumping. The plantar fascia helps support the arch of the foot, keeping the foot stable during gait, making it an essential component of foot functions. When the plantar fascia gets inflamed, it can result in significant heel pain, especially with the first steps taken in the morning.
Functions of Plantar Fascia
The plantar fascia performs several important functions for the foot:
- Arch Support: The plantar fascia helps maintain the foot arch by stabilising it when you walk or stand. This support is crucial for preventing excessive foot flattening or over-pronation
- Shock Absorption: As you walk, run, or jump, the plantar fascia absorbs much of the impact and pressure placed on the foot. It helps distribute the force more evenly across the foot to reduce strain on other structures.
- Facilitates Movement: The plantar fascia plays a significant role during push-off. It helps the foot return to its natural shape after each step, enabling efficient movement and stable propulsion.
- Reduces Muscle Stress: The plantar fascia connects the heel to the toes, providing stability and ensuring the smooth movement of the foot. Its role is to help reduce the load and stress acting on muscles within the foot.
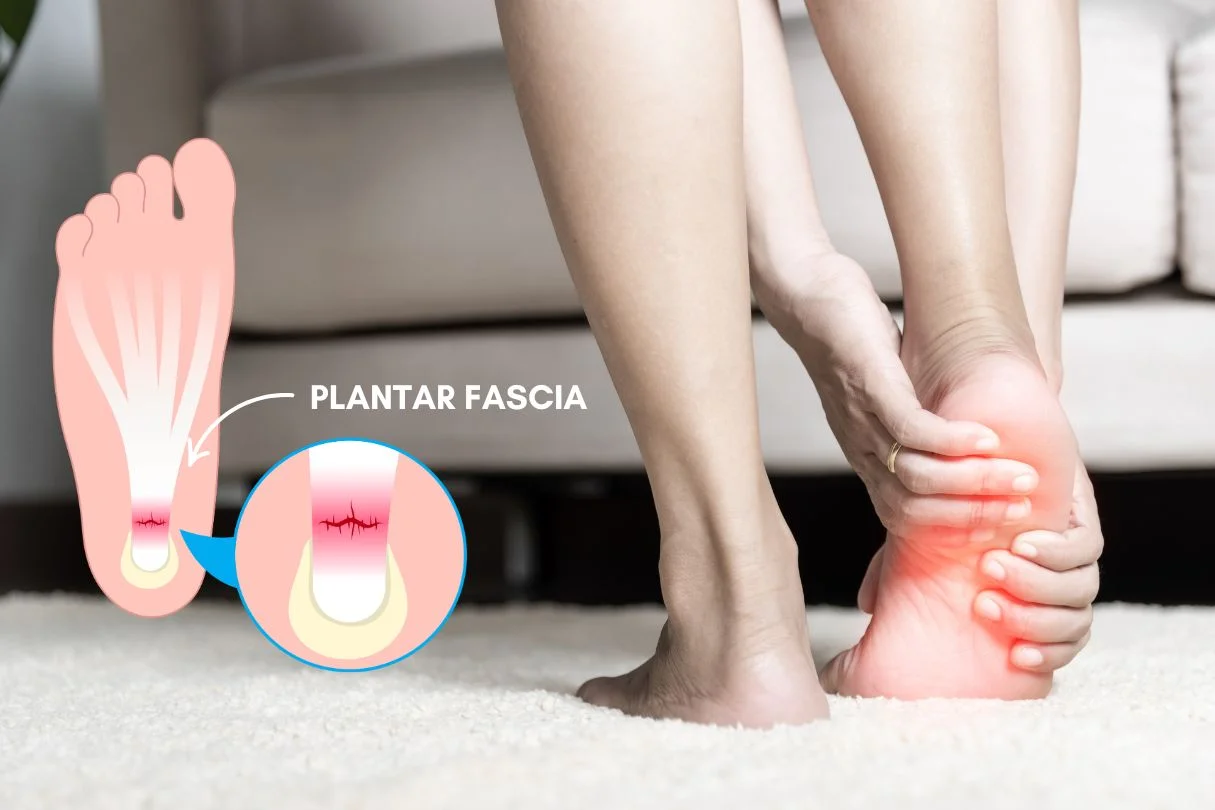
Causes of Plantar Fascia Inflammation
Plantar fascia inflammation typically results from repetitive strain or overuse. Here are some common causes:
- Overuse: High-impact activities such as running, jumping, or prolonged standing can cause irritation and inflammation of the plantar fascia.
- Improper Footwear: Wearing shoes with poor arch support or insufficient cushioning can increase stress on the plantar fascia, contributing to inflammation and discomfort.
- Obesity: Excess bodyweight can increase the load on the feet, which can strain the plantar fascia and lead to inflammation over time.
- Foot Structure Abnormalities: Certain foot deformities, such as flat feet or high arches, can affect the way your bodyweight is distributed across the foot, increasing stress on the plantar fascia and leading to inflammation.
- Tight Muscles: Tightness in the calves, Achilles tendon, or other foot muscles can put additional strain on the plantar fascia, increasing the risk of injury.
- Sudden Increase in Activity: Rapidly increasing physical activity without proper conditioning can overwhelm the plantar fascia, resulting in inflammation.
Can I Walk Without a Plantar Fascia?
Although the plantar fascia is essential for foot function, there are rare instances where it may be absent due to a history of surgical intervention. Without the plantar fascia, several issues may arise:
- Decreased Shock Absorption: Without the plantar fascia to absorb impact, the joints, bones, and muscles of the foot will have to take extra stress, leading to pain and discomfort.
- Instability: The absence of the plantar fascia may cause instability in the foot, especially during movement. This can result in gait abnormalities and even changes in the shape of the foot.
- Altered Foot Mechanics: The absence of the plantar fascia can change the way you walk, potentially causing problems in the ankle, knee, or hip due to improper alignment.
However, in cases where the plantar fascia is absent, other parts of the foot will usually compensate for its function. Custom orthotics, foot rehabilitation, and carefully managed activity can help relief discomfort and improve foot function.
How to Prevent Plantar Fascia Injury?
Preventing plantar fascia injury and inflammation is key to maintaining healthy feet. Here are some tips to help protect the plantar fascia:
- Wear Proper Footwear: Choose shoes that provide proper arch support and cushioning. Avoid high heels or shoes that lack support, as they can increase strain on the plantar fascia.
- Stretching and Strengthening: Regularly stretch your calves, Achilles tendon, and the bottom of your feet to improve flexibility and prevent tightness. Strengthening exercises for the feet and lower legs can also help protect the plantar fascia.
- Gradual Increase in Activity: If you’re increasing your physical activity, do so gradually. Sudden increases in intensity or duration can overload the plantar fascia and lead to inflammation.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can put added pressure on your feet, increasing the risk of plantar fascia injury. Maintaining a healthy weight helps reduce strain on the foot’s structures.
- Foot Rest and Recovery: Give your feet adequate rest if you’re engaging in high-impact activities. Taking breaks and incorporating low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling can give the plantar fascia time to recover.
- Use Orthotics: If you have flat feet or other structural abnormalities, consider using custom orthotics to provide additional arch support and reduce stress on the plantar fascia.
Conclusion
The plantar fascia is a vital structure in the foot that plays an essential role in supporting movement, absorbing shock, and maintaining foot stability. However, it is prone to inflammation, especially when between ages of 40 to 60s, or with repetitive strain or overuse. Understanding the functions of the plantar fascia, the causes of inflammation, and preventive measures can help protect your feet from injury. If you’re experiencing symptoms of plantar fascia inflammation, such as heel pain, discomfort, or difficulty walking, contact Straits Podiatry today for a comprehensive evaluation and personalised management plan. Our team is dedicated to helping you maintain healthy feet and an active lifestyle.
Podiatrist experienced in diabetic foot management and amputation prevention.
Jackie Tey
Chief Podiatrist, B.Pod(Hons). Your foot and lower limb specialist passionate about raising awareness for foot and lower limb health.








