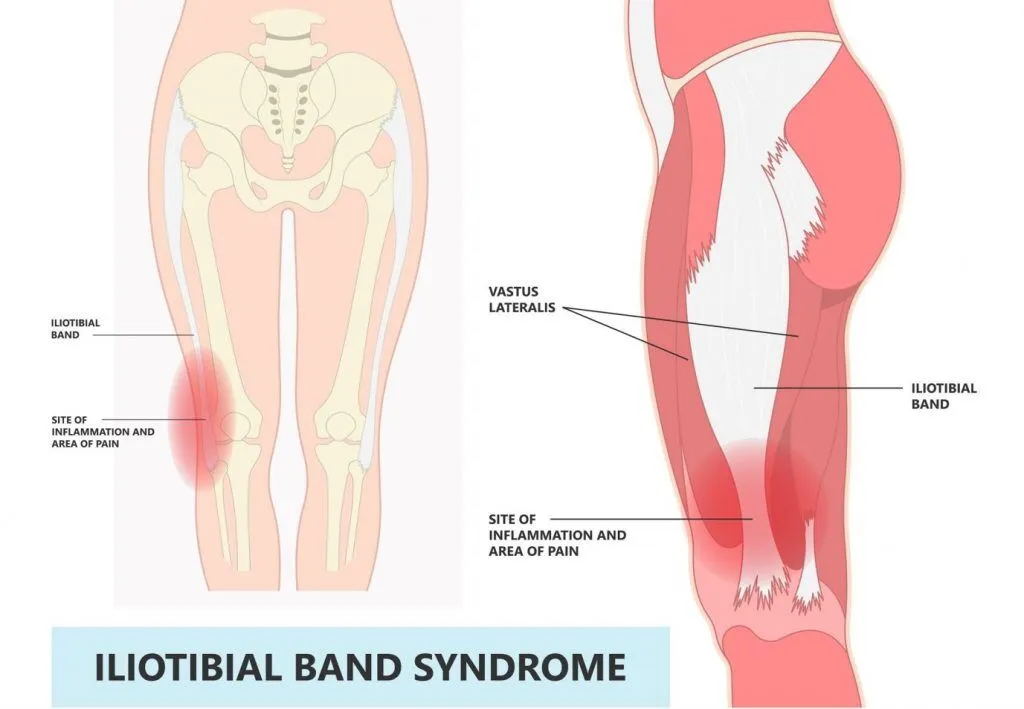
What is Iliotibial Band Syndrome (ITBS)?
Iliotibial band syndrome (ITBS) is a condition that causes pain at the lateral (outside) knee joint and is exacerbated by activity. It is an overuse condition resulting from repeated extension and flexion of the knees and therefore commonly affects runners and cyclists. It also tends to occur in individuals with a sudden increase in activity level.
The iliotibial band (ITB) is a thick fascia band that runs from the outside hip to the outside knee and helps to provide rotational stability to the hip and knee. The cause of ITBS is often multifactorial and if left untreated, it can affect your ability to walk, run or climb stairs.
Causes of Iliotibial Band Syndrome
There are 2 proposed causes of ITBS – repetitive traction and repetitive friction. Several risk factors contribute to these causes.
Repetitive traction occurs when there is an increased demand for our ITB to stabilise the rotational movements of our lower limb, especially during activity such as long-distance running, or when a person has excessive pronation. Prolonged traction creates stress on the ITB and results in pain and inflammation.
Repetitive friction occurs when the ITB constantly glides forward and backwards over a bony protrusion of the thighbone (femur), known as lateral femoral condyle. This friction creates pain and inflammation of the ITB and the bursa between these two structures.
Need Help? See A Podiatrist Today
Risk Factors of Iliotibial Band Syndrome (ITBS)
The risk factors of ITBS include:
- Repetitive activities such as running and cycling with inadequate recovery
- Sudden increase in activity
- Flat feet or excessive pronation of the foot
- Weakness of the hips, glutes or thigh muscles
- Soft tissue tightness of the hip, glute or thigh muscles
- Knock knees
- Leg length differences
Signs and Symptoms of Iliotibial Band Syndrome (ITBS)
Signs and symptoms of ITBS include:
- Sharp or burning pain at the outside of the knee
- Pain radiating to the outer thigh and/or outer shin
- Pain during activities such as running, cycling or climbing stairs
- Redness and swelling of the outside knee
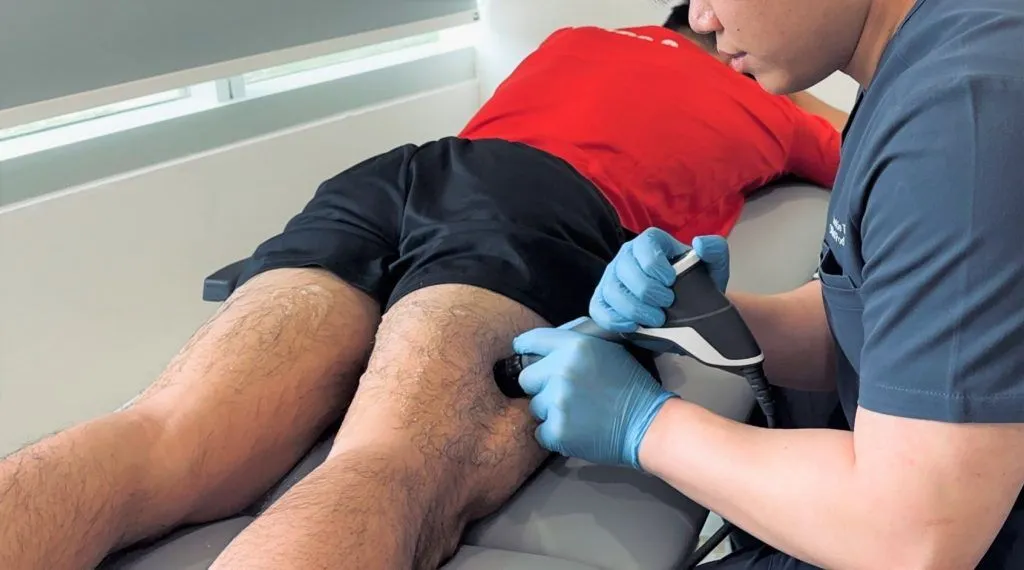
Iliotibial Band Syndrome (ITBS) Treatment in Singapore
Addressing the underlying causes of the condition is essential in reducing further stress and preventing deterioration. Depending on the severity of the condition, addressing the injured ITB will be necessary to recover properly.
Treatment options for ITBS in Singapore include:
- Customised foot orthoses to control rotational forces of the lower limb
- Extracorporeal shockwave therapy to stimulate tissue regeneration
- Radial pressure wave therapy to release muscular tension and trigger points
- Stretching and strengthening program
- Physical therapy