Rheumatoid Arthritis and Foot Health
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) can significantly impact foot health, causing discomfort and hindering mobility for those affected. Understanding the specific challenges associated with rheumatoid arthritis in the feet is crucial for appropriate treatment, prevention of progression, and pain relief. In this article, we’ll delve into essential strategies and considerations for caring for feet affected by Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune condition that can significantly affect your foot health. It is a condition that affects the joints of the feet, causing pain, stiffness, and inflammation. The feet and ankles are often the first places to be affected, making it essential to understand the symptoms and treatment options available.
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that causes inflammation in the joints, tendons, and ligaments throughout the body. It typically affects the hands and feet, but it can also affect other areas such as the neck, shoulders, elbows, knees, and hips.
Need Help? See Our Podiatrist Today
What Causes Rheumatoid Arthritis?
- Genetic Factors: Certain genetic markers, such as specific variations in the HLA (human leukocyte antigen) genes, have been linked to an increased risk of developing RA.
- Autoimmune Response: The body’s immune system mistakenly identifies its own cells as a threat, leading to attacks on the joints.
- Environmental Factors: Some research suggests that smoking, air pollution, and exposure to certain infections can increase the risk or worsen RA.
- Hormonal Factors: Hormonal changes may also influence the development of rheumatoid arthritis, as the condition is more common in women than in men.
- Other Factors: Researchers also suggest that obesity, which can increase inflammation in the body, may contribute to RA formation
Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis in the Feet
The symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis in the feet can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
- Pain and stiffness in the joints
- Swelling and tenderness in the joints
- Limited range of motion
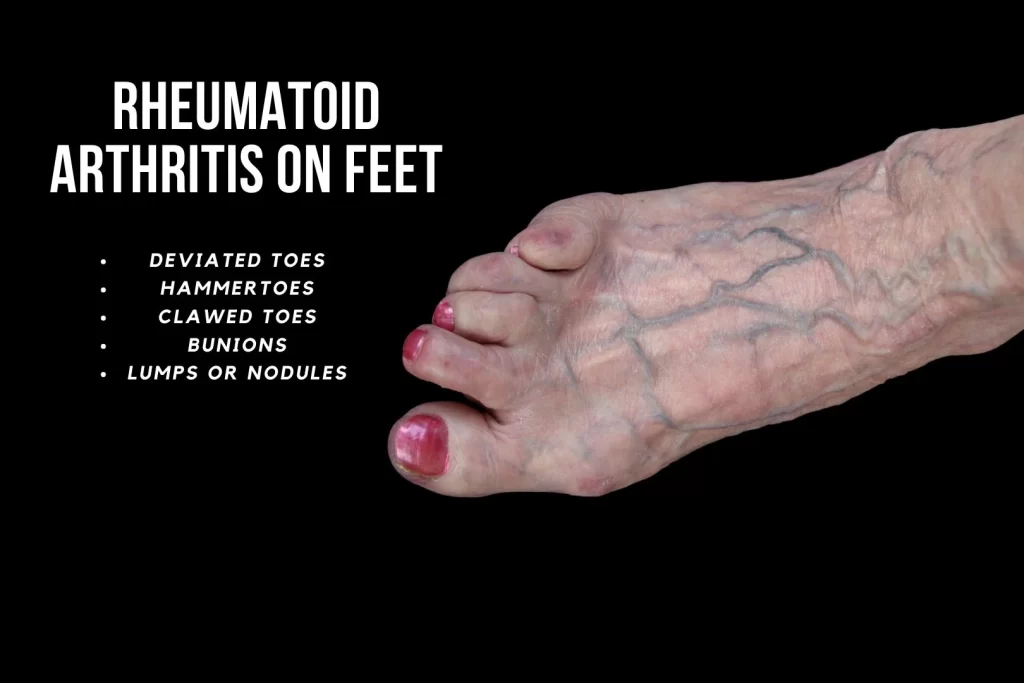
- Change in foot posture, causing flat feet deformity
- Progressive toe deformities (toes deviating outwards) and bunions formation
- Lumps or rheumatoid nodules under the skin, commonly present in weight-bearing areas
- Difficulty walking and maintaining balance
Rheumatoid arthritis can cause permanent damage to the foot joints and lead to disability if appropriate treatment and management are not given.
Diagnosing Rheumatoid Arthritis
Treatment Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis in The Feet
Rheumatoid arthritis typically requires medications to control its disease progression. For rheumatoid arthritis in the feet, several treatment options are available to prevent or delay the formation of progressive foot deformities. Treatment options available in Singapore may include:
- Customised foot orthotics: Custom insoles play an important role in managing RA in the feet. They can help to provide support and prevent changes in foot shape. They can also help to accommodate existing deformities to relieve pain and provide stability.
- Physical therapy: Stretching and strengthening exercises are vital to maintaining mobility, strength and range of motion.
- Shockwave therapy: Early research suggests that shockwave therapy can help reduce pain and morning stiffness, providing symptomatic relief.
- Surgery: Surgery can help to correct painful deformities in severe cases that do not respond to conservative management.
Podiatry For Rheumatoid Arthritis In The Feet
At Straits Podiatry, we recognise the importance of a multidisciplinary approach to managing rheumatoid arthritis in the feet. Our team of podiatrists works closely with rheumatologists, physical therapists, and other healthcare providers to tailor management plans to each individual patient
If you are experiencing symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis in your feet, do not hesitate to contact us at Straits Podiatry in Singapore. Our team of expert podiatrists has the knowledge and experience to provide the care and treatment you need to manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life. With our state-of-the-art facilities and comprehensive approach to foot health, we can help you achieve optimal foot health and wellness. Contact us or schedule an appointment today!
Share this with someone you know
Frequently Asked Questions About Rheumatoid Arthritis
Is Rheumatoid arthritis the same as osteoarthritis?
No, RA and osteoarthritis (OA) are two different types of arthritis with distinct causes and characteristics. RA is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks the body’s own joints and soft tissue, leading to inflammation, joint damage, and systemic symptoms. Osteoarthritis, on the other hand, is a degenerative joint disease resulting from wear and tear on the joints over time, leading to cartilage breakdown, joint pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. While both conditions can cause joint pain and stiffness, they have different underlying mechanisms and require different approaches to treatment.
Can rheumatoid arthritis affect children's feet?
What lifestyle changes can help manage rheumatoid arthritis?
Search
You May Also Like
Do You Have A Question? Ask Us...
Search
Do You Have A Question? Ask Us...
You May Also like
Categories
Categories
- Ankle (4)
- Diabetic Foot (7)
- Feet (5)
- Knee (5)
- Paediatric Lower (5)
- Soft Tissue (3)
- Uncategorized (60)